Microneedling vitamins: what works, what burns, what heals
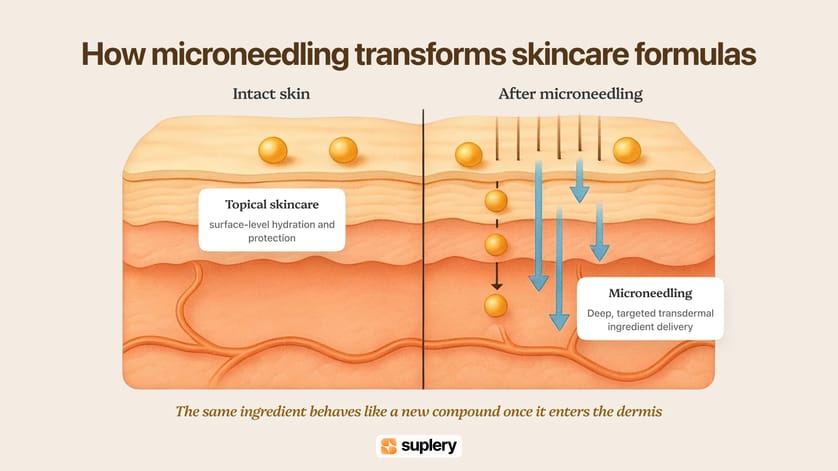
Microneedling changes every rule you know about skincare formulas. The moment you open microchannels, a vitamin stops acting like a surface-active ingredient and starts behaving like a transdermal compound — reaching layers where stability, pH, purity, and molecular weight matter far more than the label suggests.
This is where pros run into real challenges: the same vitamin C that brightens beautifully on intact skin can sting inside microchannels; the retinoid that boosts collagen in a routine may overwhelm the dermis when delivered deeper; even a gentle niacinamide serum can shift behavior depending on pH and formulation. These differences aren’t intuitive — and the industry rarely explains them.
This guide clears the noise. You’ll see exactly how each vitamin family behaves when used with microneedling, which forms are safe or effective, which ones need caution, and how to choose working, treatment-ready formulas instead of guessing. Clean structure, high-density insights, evidence-backed logic — created specifically for pros who want predictable results and confident decisions in every treatment.
What makes a vitamin microneedling-safe🔬
Choosing vitamins for microneedling is not the same as choosing vitamins for topical skincare. One formula supports collagen production, brightens tone, and calms inflammation — another formula, with the same vitamin name on the label, triggers irritation once delivered into the dermis. The difference is hidden in seven technical details that most brands don’t disclose, but every professional needs to understand before opening microchannels.
Sterility and purity 🔬
Microneedling delivers everything deeper — the active, the base, the preservatives, the fragrance compounds, the microscopic particles in the formula. Only sterile or injection-grade serums are designed for this environment. Anything with fillers, essential oils, fragrance, or suspended particles introduces unpredictable risk.
pH and skin compatibility 🧪
Once microchannels are open, pH stops being a comfort preference and becomes a biological requirement. Low pH formulas that feel tolerable on the surface can sting deeply when infused into the dermis. For vitamins, a working pH range of 4.5–6.0 is the safest zone, unless the active explicitly requires otherwise.
Supporting ingredients ⚗️
A vitamin is only as safe as the formula around it. Alcohols, perfumes, harsh preservatives, plant proteins, thick oils, or any ingredient not designed for percutaneous infusion can disrupt healing. Simplified, minimal INCI lists are essential for microneedling work.
Concentration shifts 📈
A 10% serum on intact skin behaves like a 10% serum. After microneedling, it behaves like a much higher dose — because more of it reaches the viable layers. High-strength retinoids or acidic vitamin C become dramatically more reactive. Gentle, buffered, and stabilized forms perform better and recover faster.
Stability and packaging 📦
Unstable vitamins oxidize, degrade, or shift pH — and degraded actives behave unpredictably inside microchannels. Fresh, airtight, light-protected ampoules or single-use packaging protect integrity and reduce post-treatment reactions.
Irritation potential 🩹
Some vitamins initiate mild controlled inflammation — great on intact skin, aggressive when introduced into an already-inflamed environment. Knowing the irritancy profile of each form matters more here than in any other treatment category.
Prescription-only restrictions ⚠️
Anything classified as a drug (retinoic acid, certain vitamin D analogs) belongs exclusively to medical protocols. Their penetration is too strong, their effects too potent, and their risks too high for cosmetic microneedling.
Together, these factors define whether a vitamin becomes a powerful treatment tool — or an avoidable complication. Understanding them sets the foundation for choosing each vitamin family with precision, confidence, and clear intention.
🧬 Vitamin A: your strongest tool — and your sharpest edge
Retinoids are the backbone of pro-aging treatments, collagen induction, acne protocols, and scar work — but with microneedling, their behavior changes dramatically. Every form of Vitamin A has a different level of potency, stability, irritation potential, and dermal behavior. Understanding these differences is what separates predictable, controlled results from aggressive inflammatory reactions.
What Vitamin A actually does inside the skin
Retinoids accelerate cell turnover, stimulate fibroblasts, regulate oil flow, soften texture, and support long-term collagen remodeling. In microneedling, these benefits amplify — because the molecule reaches deeper, faster, and in greater concentration than during topical use. This amplification works both ways: stronger results and higher irritation risk.
Evidence snapshot
Clinical research consistently shows improved collagen synthesis, acne scar reduction, and textural refinement when retinoids are paired with controlled dermal delivery — but only when the correct form is used. Stronger forms (like tretinoin) show impressive outcomes in medical settings, while esthetic protocols rely on gentler, more stable esters with fewer inflammatory spikes.
Forms, strengths, and stability — what matters most
Different retinoids behave completely differently once delivered through microchannels:
Retinyl esters (retinyl palmitate, retinyl acetate, retinyl propionate)
- Safest vitamin A forms for microneedling
- Low irritation, stable, slow conversion
- Ideal for “during-needling” infusion
- Suitable for sensitive skin and first-time retinoid clients Best use: anti-aging, barrier-friendly rejuvenation, early acne care
Retinol (0.25–1%)
- Potent and effective, but reactive when delivered too deep
- Amplified irritation after needling
- Works well after healing begins — not during Best use: scar repair, texture refinement, pro-aging maintenance, but only 48–72 hours post-procedure
Retinaldehyde (retinal)
- Faster-acting than retinol
- Less stable, more likely to irritate in microchannels
- Limited professional data on direct needling use Best use: post-treatment only, in low concentrations, for experienced skin
Retinoic acid (tretinoin)
- Medical potency
- Extremely high irritation risk when delivered transdermally
- Can create peel-like reactions, PIH, or excessive inflammation Best use: strictly medical microneedling protocols under physician supervision
pH and formulation rules
Retinoids are most stable around pH 5–6, which aligns well with microneedling. Instability increases dramatically in acidic environments — a key reason to avoid combining retinoids with low-pH vitamin C during or immediately after treatment.
What to expect on skin
- Mild, controlled inflammation with esters
- Noticeable redness and flaking with retinol
- High likelihood of irritation with retinal
- Strong peeling and prolonged erythema with tretinoin
Microchannels increase dermal exposure, so even a normally comfortable concentration can feel drastically stronger.
Microneedling takeaway
Use during treatment: Retinyl esters (palmitate, acetate) — stable, slow, safe
Use after treatment (48–72h later): Low-strength retinol — controlled resurfacing without overwhelming inflammation
Avoid for cosmetic microneedling: Retinal, tretinoin, any prescription-strength A-form
One-line memory formula
During needling → esters. After healing → gentle retinol. Medical depth → tretinoin only with an MD.
🛡️Vitamin B: the calm, steady workhorses of microneedling
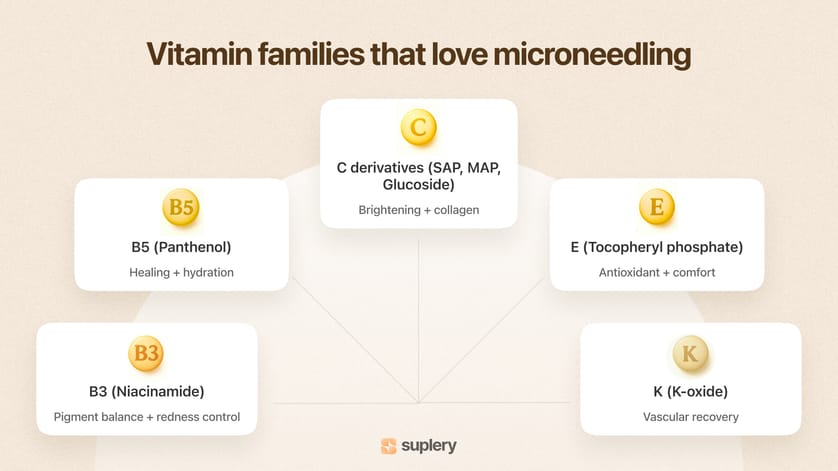
B-vitamins behave differently from A and C: they don’t spike irritation, they don’t destabilize formulas, and they don’t provoke unpredictable reactions inside microchannels. Instead, they support healing, balance inflammation, and strengthen the barrier — exactly what the skin needs before, during, and after needling. The two stars of this category are niacinamide (B3) and panthenol (B5), each backed by strong evidence and excellent tolerance.
Niacinamide (B3) — stability, clarity, and barrier support
Niacinamide is one of the most microneedling-friendly vitamins: small molecule, water-soluble, neutral pH, and naturally anti-inflammatory. It reduces redness, regulates sebum, supports ceramide production, fades discoloration, and strengthens the barrier. Inside microchannels, it penetrates quickly without triggering irritation spikes, making it ideal for concerns like PIH, pigment control, acne-prone skin, or sensitivity.
Its acidic sibling, niacin, causes a strong flushing response — amplified dramatically by microneedling — and doesn’t belong anywhere near dermal entry.
Use during and after treatment: Yes Best for: inflammation control, pigment, oil regulation, barrier repair Avoid: any formula where B3 is paired with acids at very low pH (risk of niacin formation during storage)
Panthenol (B5) — the recovery accelerator
Panthenol converts into pantothenic acid in the skin and excels at hydration, wound repair, and calming. It improves barrier recovery, reduces erythema, increases fibroblast proliferation, and speeds the closure of microchannels. Its stability, gentle profile, and predictable penetration make it one of the safest and most effective vitamins for immediate post-needling use.
This is the vitamin you want in every recovery phase — it soothes without suppressing the controlled inflammation needed for collagen induction.
Use during and after treatment: Yes Best for: healing, hydration, redness reduction, barrier repair Irritation risk: extremely low
Other B vitamins
- B6 (pyridoxine): niche, mild anti-inflammatory support
- B7 (biotin): minimal skin penetration topically; used mostly in scalp cocktails
- B9 (folic acid): supports DNA repair; works better delivered through microchannels
- B12: anti-inflammatory, but large molecule; best for targeted professional use
These can be “bonus” actives in professional cocktails but are not essential to most protocols.
Microneedling takeaway
B-vitamins are the most forgiving category: stable, biocompatible, non-reactive, and synergistic with wound healing. Niacinamide and panthenol form the backbone of safe, versatile microneedling formulas that calm, repair, and support the skin through every phase of the treatment.
One-line memory formula
B3 for balance — B5 for healing. Everything else is optional.
✨ Vitamin C: brilliance, chemistry, and the art of choosing the right form
Vitamin C is one of the most searched, most requested, and most overused actives in microneedling — and also the one where formulation mistakes show up fastest. It can brighten, support collagen, improve tone, and enhance antioxidant protection. But once delivered through microchannels, its pH, stability, and molecular form become non-negotiable.
What Vitamin C actually does
Inside the dermis, Vitamin C acts as a co-factor for collagen synthesis, reduces oxidative stress from controlled microinjury, and helps fade pigment irregularities. When delivered deeper, these benefits intensify — but only if the molecule is intact, stable, fresh, and at the right pH.
Pure L-ascorbic acid: powerful but aggressive
LAA is the gold standard for collagen support and brightening, but it only stays stable and absorbable at a very low pH (≈2.5–3.5). On intact skin, this just feels tingly. Inside microchannels, that same acidity can feel like a burn.
It’s potent, but volatile: easily oxidizes, darkens, destabilizes, and becomes far more reactive when delivered past the epidermal barrier. Clinical protocols exist, but they’re strictly professional, tightly controlled, and require fresh, sterile product.
Use during treatment: Only in controlled, professional protocols Use after treatment: Only once healing begins, and only with stable, fresh formulas Risk: irritation, PIH, sting, oxidation-related reactivity
Stabilized derivatives: the real microneedling heroes
Most of the Vitamin C that performs well with microneedling comes from non-acidic, stable, enzyme-activated derivatives. These enter the skin calmly, convert gradually, and provide long-term antioxidant and brightening benefits without the acid burn.
Sodium Ascorbyl Phosphate (SAP)
- Very stable at neutral pH
- Anti-acne, pigment-evening, calming
- Excellent tolerance inside microchannels Best for: acne-prone skin, pigment, maintenance
Magnesium Ascorbyl Phosphate (MAP)
- Stable, gentle, barrier-friendly
- Slow, steady brightening Best for: sensitive skin, first-time Vitamin C clients
Ascorbyl Glucoside
- Good stability, water-soluble
- Gradual release, balanced results Best for: all skin types needing clarity and even tone
3-O-Ethyl Ascorbic Acid
- Newer, potent, more penetrating
- Works at slightly acidic but comfortable pH Best for: pro-aging and pigment work without the harshness of LAA
Tetrahexyldecyl Ascorbate (THD)
- Lipid-soluble, deeply penetrating
- Stable and gentle even on reactive skin
- Needs proper formulation to infuse through microchannels Best for: deeper rejuvenation, mature and dry skin
Formulation and pH rules
Stable forms allow you to work in the ideal microneedling pH zone (4.5–6.0) — significantly reducing the sting and inflammatory response. Low-pH formulas belong exclusively to controlled professional settings, not routine cosmetic microneedling.
Microneedling takeaway
Non-acidic, stable Vitamin C derivatives deliver the best results with the lowest risk. They brighten, support collagen, and strengthen the skin while keeping inflammation predictable and recovery smooth.
Use during treatment: SAP, MAP, ascorbyl glucoside, ethyl ascorbic Use post-treatment: THD, low-concentration LAA once channels close Avoid: oxidized serum, old serum, any product with visible color shift or low-pH sting
One-line memory formula
For microneedling: stability wins, acidity complicates everything.
🌿 Vitamin D: a quiet nutrient with a limited — but specific — role
Vitamin D is essential for skin physiology, immunity, and barrier integrity, but in professional cosmetics it plays a surprisingly small role. Most formulas contain only trace amounts, and most clinical research around dermatology uses prescription-only analogs — not cosmetic Vitamin D. For microneedling, the key is understanding where it helps, where it doesn’t, and why it rarely appears in standard esthetic cocktails.
What Vitamin D actually does in skin
Vitamin D supports keratinocyte differentiation, immune balance, and barrier repair. In medical dermatology, active Vitamin D analogs help normalize cell behavior and reduce inflammatory overgrowth (psoriasis is the classic example). In cosmetic skincare, Vitamin D acts more as a barrier-supportive nutrient than a performance-driven active.
Forms you’ll see
Most cosmetic formulas use cholecalciferol (Vitamin D₃) — a fat-soluble, oil-phase ingredient that provides light nourishment but minimal targeted action. The forms that actually change skin behavior — calcitriol and calcipotriol — are prescription medications with measurable biologic activity.
These medical forms should never be pushed into microchannels outside of a physician-directed protocol.
Penetration behavior
Because Vitamin D is lipid-based, it stays mostly in the epidermis when applied topically. Microneedling can push it deeper, but this does not meaningfully enhance results for routine esthetic concerns. Vitamin D’s benefits come from long-term barrier support, not quick dermal delivery.
In other words: deeper penetration doesn’t equal more visible impact here.
When Vitamin D is actually useful
There are two specific niches where Vitamin D shows relevance:
Barrier repair
Skin with significant dryness, flaking, or chronic irritation may benefit from formulas that include Vitamin D₃ as part of a broader lipid-support blend. Microneedling doesn’t dramatically amplify this benefit, but it doesn’t interfere either.
Scalp and hair protocols (medical)
Some dermatologists use Vitamin D analogs in alopecia protocols. This is strictly medical and not performed in esthetic microneedling settings.
When to avoid Vitamin D
Avoid any prescription-level Vitamin D during cosmetic microneedling. These analogs can influence calcium metabolism and cellular behavior more intensely than most vitamins — appropriate only within medical supervision.
Microneedling takeaway
Vitamin D is not a key microneedling vitamin. It’s supportive but not transformative, and it brings no additional value from deep dermal infusion. Treat it as a background nutrient — not a main active.
Use during treatment: unnecessary, optional Use after treatment: fine in barrier creams or oils Avoid: calcitriol, calcipotriol, or any prescription analogs
One-line memory formula
Vitamin D supports the barrier — but isn’t a microneedling-active vitamin.
Printable client cards: Your 24-hour skincare plan
Download, print, and hand out after each treatment — two professional morning and evening routine cards that help clients maintain their glow, stay consistent with your recommendations, and build lasting trust in your expertise.
Oh no! We couldn’t subscribe you ☹️
Done! We've sent a link to your Email 📨
🧴Vitamin E: lipid protection and calm support inside microchannels
Vitamin E is one of the most reliable antioxidant supports in professional skincare. It protects lipids, calms irritation, softens inflammation, and reinforces the barrier — exactly the kind of work skin needs during and after microneedling. But Vitamin E isn’t one molecule; its behavior depends on the form, stability, and how it’s delivered.
What Vitamin E actually does
Inside the skin, Vitamin E neutralizes lipid peroxides, reduces oxidative stress after microinjury, and strengthens barrier recovery. It integrates into cell membranes, supports moisture retention, and acts as a buffer against irritation triggered by other actives used in the protocol.
In microneedling, these benefits matter even more because the lipid matrix becomes temporarily vulnerable.
Forms that behave well in microneedling
Tocopherol (alpha-tocopherol)
Biologically active and effective, but naturally unstable. Oxidizes quickly when exposed to air or light — meaning it must be fresh and protected.
Works beautifully when delivered in a light, controlled formulation with proper stabilization.
Tocopheryl Acetate
The most stable and widely used form. Gentle, predictable, slow to convert to active E, but excellent for barrier comfort during recovery.
Ideal when the goal is soothing and long-term protection rather than immediate antioxidant intensity.
Tocopheryl Phosphate
A water-compatible derivative that blends easily into microneedling serums. Stable, gentle, and effective inside microchannels.
One of the best choices when you want Vitamin E without an oily base.
Tocotrienols
Potent antioxidant members of the Vitamin E family. Less common in standard formulations, but valuable in advanced rejuvenation blends.
Formulation behavior
Vitamin E performs best in:
- light emulsions
- lipid serums designed for dermal entry
- stabilized blends with Vitamin C derivatives
- post-needling barrier creams
Pure Vitamin E oils or thick, occlusive bases are too heavy for open microchannels and can interfere with healing.
Microneedling takeaway
Vitamin E brings stability and comfort to microneedling — when the formula is clean, light, and designed for dermal-level delivery. It shields the skin from oxidative stress, supports recovery, and pairs well with Vitamin C derivatives and B vitamins.
Use during treatment: tocopheryl phosphate, stabilized tocopherol blends Use immediately after treatment: tocopheryl acetate, gentle emulsions Avoid: thick occlusive Vitamin E oils, heavy butters, or oxidized formulas
One-line memory formula
Vitamin E protects the lipids that protect the skin — especially when microchannels are open.
🩸Vitamin K: vascular repair and faster recovery where it matters
Vitamin K operates in a different part of the skin biology landscape than A, B, C, or E. Its impact isn’t on pigment pathways, barrier lipids, or collagen stimulation — it works on something deeper and more structural: the microvasculature. That’s why Vitamin K becomes especially relevant in microneedling, where pinpoint bleeding, bruising, and capillary reactivity can affect both results and recovery.
What Vitamin K actually does
Vitamin K supports proper blood flow behavior and helps clear residual blood pigments that contribute to lingering redness, under-eye darkness, and post-procedure bruising. In the dermis, these effects become stronger because Vitamin K acts close to the capillary networks responsible for color, swelling, and recovery time.
Without microneedling, Vitamin K barely reaches the layers where it can do this work. With microchannels open, it finally has access to its ideal target zone.
The forms that matter
Phytonadione (Vitamin K1)
The most researched cosmetic form. Helps fade vascular discoloration and reduces the appearance of purple or bluish tones.
Ideal for eye-area work, post-injection recovery, and any treatment where capillary reactivity shows up strongly.
Vitamin K oxide
A stabilized form engineered for better penetration and higher effectiveness. Frequently used in professional bruise creams and under-eye protocols.
More predictable and longer-lasting than pure K1 inside cosmetic formulas.
Vitamin K2 (menaquinones)
Occasionally used but less documented in dermal applications. Can be included but not essential for microneedling.
Where it shines in microneedling
✔️ Under-eye microneedling: targeted work for vascular dark circles ✔️ Post-needling redness: faster return to even tone ✔️ Pinpoint bleeding areas: supports quicker clearance ✔️ Bruise-prone clients: especially after combined procedures ✔️ Rosacea-adjacent redness: supportive, calming presence (not a treatment, but helpful)
These effects compound with B3 (niacinamide) and Vitamin C derivatives — a strong trio for clarity and tone refinement.
Formulation behavior
Vitamin K is fat-soluble, so it performs best when:
- encapsulated
- stabilized in emulsions
- paired with lightweight lipids
- formulated without fragrance or irritant botanicals
Microneedling pushes these forms deeper, giving Vitamin K access to the dermal capillary bed — the layer where it makes the strongest visible difference.
Microneedling takeaway
Vitamin K is a vascular-focused active that becomes dramatically more effective when delivered through microchannels. It improves recovery, supports tone evenness, and reduces visible traces of procedure-induced redness or purplish hues.
Use during treatment: lightweight emulsions with K1 or K-oxide Use after treatment: soothing, stabilized K blends for recovery Avoid: heavy balms or thick occlusives containing Vitamin K — too dense for open channels
One-line memory formula
Vitamin K works where the capillaries live — and microneedling finally gets it there.
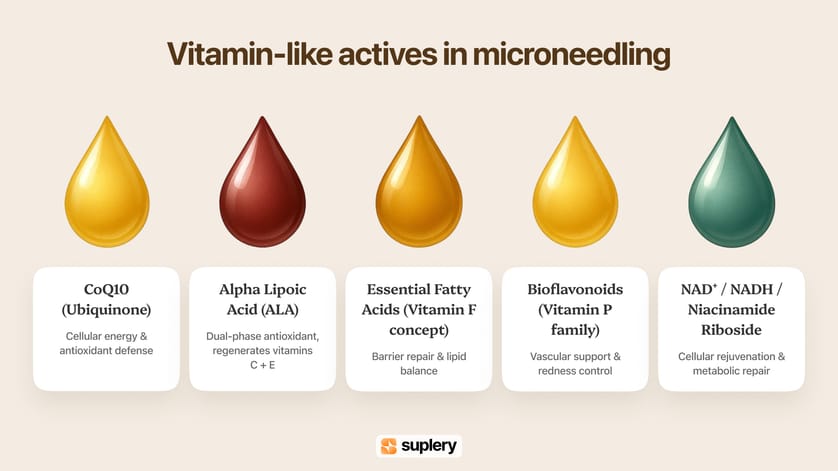
⚡ Vitamin-like actives: the silent performance boosters inside microchannels
Some of the most effective ingredients in microneedling aren’t technically vitamins — they’re coenzymes, antioxidants, metabolic boosters, or structural lipids that work deeper than surface formulas allow. These molecules often struggle to penetrate intact skin because of size, polarity, or stability. Microneedling changes that dynamic completely.
When delivered through microchannels, vitamin-like actives finally reach the layers where they can fuel cellular energy, protect collagen, support recovery, and stabilize the results of more potent vitamins.
CoQ10 (Ubiquinone) — energy, antioxidant defense, dermal strength
CoQ10 is large in size and naturally stays in the upper epidermis, which limits its benefits in topical skincare. Inside microchannels, its behavior shifts dramatically: it reaches fibroblasts, supports mitochondrial energy, and helps reduce oxidative stress generated during controlled injury.
This makes CoQ10 a quiet but meaningful addition to pro-aging, texture, and recovery protocols.
Use during treatment: in nanoemulsions or light serums Best for: collagen support, dullness, mature skin Note: yellow tint is normal — it doesn’t stain skin
Alpha Lipoic Acid (ALA) — multi-phase antioxidant with clinical edge
ALA is one of the few antioxidants that is both water- and fat-soluble, giving it access to multiple skin compartments. It enhances the antioxidant network, regenerates vitamins C and E, and reduces visible inflammation. It can tingle on intact skin — through microchannels this sensation intensifies, so concentrations must be controlled.
Use during treatment: low % only (professional) Use after treatment: gentle formulas, once irritation settles Best for: redness-prone clients, oxidative stress, pro-aging protocols
Essential Fatty Acids (Vitamin F concept) — barrier architecture
Linoleic and linolenic acids aren’t vitamins in the classical sense, but they are essential nutrients for barrier function. They restore ceramide pathways, reduce TEWL, and prevent micro-flaking after needling. While oils are too heavy for open channels, EFAs shine once the barrier begins closing.
Use after treatment (24–48h): lightweight oils or emulsions Best for: dryness, barrier repair, sensitivity Avoid during needling: occlusive textures
Bioflavonoids (Vitamin P family) — vascular and antioxidant synergy
Rutin, hesperidin, and quercetin support microcirculation, stabilize capillaries, and reduce oxidative stress. They enhance the work of Vitamin K in vascular-focused microneedling and help refine tone around the eyes and cheeks.
Use during or after treatment: yes, in clean emulsions Best for: redness, vascular pigmentation, bruising-prone skin
NAD+, NADH, and niacinamide riboside — cellular energy boosters
These coenzymes sit at the center of cellular repair, regeneration, and longevity pathways. They are large, polar, and nearly impossible to deliver deep enough through topical use. Microneedling changes that, giving them access to metabolically active layers where recovery and collagen remodeling take place.
Use during treatment: emerging protocols only (pro-level) Use after treatment: safe in gentle serums Best for: aging skin, impaired healing, advanced pro-aging clients
Peptides and growth factors
Peptides regulate repair signals, hydration, firmness, and inflammation. Growth factors directly influence cellular behavior. Both categories benefit enormously from microneedling because they otherwise struggle to penetrate.
Use during treatment: sterile, clinique-grade only Best for: scars, aging, compromised skin Note: require high formula purity and zero irritants
Microneedling takeaway
Vitamin-like actives are optional in basic protocols but transformative in advanced ones. They amplify energy, recovery, and antioxidant defense — especially when delivered to the dermis. These actives work best when the formula is sterile, simple, and built for controlled delivery.
One-line memory formula
Think of these as boosters: CoQ10 for energy, ALA for defense, EFAs for repair, flavonoids for circulation, NAD+ for rejuvenation.
Microneedling cocktails by skin concern: your fast decision map
Microneedling is most effective when formulas are chosen based on concern + vitamin form + timing. Below are quick, clear decision maps that give you professional logic — not rigid protocols. Everything is built on stability, pH, the biological behavior of each vitamin, and clinical observations.
🔶 1. Pigmentation & tone irregularities
Goal: brighten, reduce uneven tone, support collagen, minimize PIH.
During treatment
- Niacinamide (B3) — balances pigment transfer, calms redness
- Sodium Ascorbyl Phosphate (SAP) — stable pigment control
- Magnesium Ascorbyl Phosphate (MAP) — for sensitive skin
- Vitamin K1 / K-oxide — vascular pigment, under-eye tone
After treatment (48–72h)
- 3-O-Ethyl ascorbic acid — deeper brightening without acid burn
- THD Ascorbate — lipid-phase antioxidant, long-term clarity
- Retinol 0.25–0.5% — careful resurfacing once skin is calm
Skip: LAA during treatment (pH too low), retinal, tretinoin.
Memory formula: B3 + SAP = even tone. Add THD later for deeper clarity.
🔶 2. Acne-prone skin & post-acne marks
Goal: calm inflammation, regulate oil, prevent PIH, support healing.
During treatment
- Niacinamide (B3) — sebum balance + inflammation control
- SAP (5%) — anti-acne effect + pigment prevention
- Panthenol (B5) — keeps barrier stable
- Tocopheryl phosphate — antioxidant without oil load
After treatment
- Ascorbyl glucoside — gentle brightness
- Low-dose retinol — for texture/scarring (after 48–72h)
Skip: Vitamin E oils, biotin, low-pH C, heavy textures.
Memory formula: B3 + SAP + B5 = the safest acne cocktail.
🔶 3. Scars, fine lines, texture refinement
Goal: collagen support, fibroblast activation, deeper rejuvenation.
During treatment
- Retinyl esters (palmitate/acetate) — safest Vitamin A delivery
- CoQ10 nanoemulsion — mitochondrial support for new collagen
- Niacinamide — balances repair + reduces redness
After treatment
- Retinol (0.25–1%) — controlled resurfacing
- Ethyl ascorbic acid — brightening and collagen co-factor
- Panthenol — minimizes irritation during remodeling
Skip: tretinoin (unless medical), retinal, unstable C.
Memory formula: Esters in-session, retinol after healing.
🔶 4. Redness, reactive skin, rosacea-adjacent concerns
(Not a treatment — a supportive approach for sensitive skin.)
During treatment
- Panthenol (B5) — reduces erythema
- Niacinamide (B3) — restores barrier
- Vitamin K1 or K-oxide — supports vascular tone
- Bioflavonoids (rutin/hesperidin) — capillary stability
After treatment
- MAP — gentle brightening with no sting
- Tocopheryl acetate — calm antioxidant support
Skip: ALA during treatment, low-pH acids, retinoids until barrier recovers.
Memory formula: B5 + K + flavonoids = calm, controlled recovery.
🔶 5. Under-eye area (darkness, thin skin, vascular tone)
Goal: minimize vascular pigment, support thin dermis, reduce long redness.
During treatment
- Vitamin K1 or K-oxide — best-in-class vascular ingredient
- Niacinamide — strengthens barrier + pigment modulation
- SAP — safe brightening
After treatment
- THD Ascorbate — deeper antioxidant support
- Peptides — if part of sterile eye ampoule
Skip: pure LAA, retinoids (until healed), oils.
Memory formula: K + B3 + SAP = the under-eye trio that actually works.
🔶 6. Dryness, compromised barrier, post-procedure sensitivity
Goal: rebuild moisture balance, reduce TEWL, support recovery.
During treatment
- Panthenol (B5) — hydration + repair
- Tocopheryl phosphate — antioxidant comfort
- Niacinamide — barrier lipids
After treatment (24–48h)
- Essential fatty acids (linoleic-rich oils)
- Tocopheryl acetate
- Folic acid (B9) — barrier renewal support
Skip: retinol immediately, acids, low-pH C.
Memory formula: B5 now, EFAs later.
🔶 7. Hair/scalp microneedling
Goal: circulation support, follicle nutrition, scalp strength.
During treatment
- Niacinamide — scalp barrier, sebum balance
- B-complex (B6, B7, B12) — follicle support
- CoQ10 — energy for follicles
- SAP — safe anti-inflammatory effect
Professional-only (medical)
- Vitamin D analogs
- Prescription retinoids
- Mesotherapy cocktails
Memory formula: B-complex + niacinamide + CoQ10 = universal scalp support.
The takeaway: precision wins
Microneedling works when every choice is intentional — concern, vitamin form, timing. Now you have the structure for all three. Use it, and every treatment becomes predictable, stable, and high-performing.
And when you’re ready to stock formulas that match this level of precision — Suplery Marketplace is where you’ll find the professional products built for results.
 Elevate your glow with proven beauty secrets
Elevate your glow with proven beauty secrets
Dive in now for the latest beauty hacks, expert-approved tips, and transformative routines!
Oh no! We couldn’t subscribe you ☹️
Done! You've subscribed 💛
Unsubscribe anytime. Your data is stored for business-to-business communication purposes. See our Privacy policy.
Frequently asked questions
What are microneedling vitamins and why do they work differently than topical skincare?
Microneedling vitamins are active ingredients formulated to be used alongside microneedling treatments, where microchannels allow deeper penetration into the skin. Once these channels are open, a vitamin no longer behaves like a surface skincare ingredient — it interacts directly with skin cells, the dermis, and the skin’s healing process. This shift changes everything: concentration, pH, molecular weight, and formulation stability become critical for overall skin health and safety.
Which vitamins are safe to use during microneedling treatments?
The safest microneedling vitamins are those with low irritation potential, stable pH, and clean formulations:
- Vitamin B3 (niacinamide) — supports skin barrier, reduces inflammation, balances oil
- Vitamin B5 (panthenol) — accelerates wound healing and keeps skin hydrated
- Stabilized Vitamin C derivatives like sodium ascorbyl phosphate or magnesium ascorbyl phosphate
- Vitamin E derivatives such as tocopheryl phosphate
- Vitamin K (K1 or K-oxide) for vascular repair and post-procedure redness
These vitamins support skin repair, collagen synthesis, and antioxidant protection without overwhelming sensitive or irritated skin.
Is vitamin C safe for microneedling?
Yes — but only the right form.
Pure L-ascorbic acid requires a very low pH and can trigger irritation when delivered through microchannels. In contrast, stabilized forms like:
- Sodium ascorbyl phosphate
- Ascorbyl glucoside
- 3-O-ethyl ascorbic acid
- Tetrahexyldecyl ascorbate
provide brightening, antioxidant properties, and support collagen production while keeping the skin calm and compatible with microneedling.
Can microneedling stimulate collagen production?
Yes. Microneedling is also known as collagen induction therapy because it triggers a controlled wound healing response. This process stimulates fibroblasts, increases collagen synthesis, and improves skin elasticity, skin firmness, and texture.
Vitamins such as Vitamin C, Vitamin A esters, and growth factors can further boost collagen production when used correctly during or after treatment.
What is the role of vitamin A in microneedling?
Vitamin A supports cell turnover, skin rejuvenation, and collagen remodeling — but it must be chosen carefully.
- Retinyl esters are safe during microneedling
- Retinol should be used only after healing begins
- Retinoic acid (tretinoin) is reserved for medical protocols
Using the wrong form can increase irritation, disrupt the skin barrier, and delay the healing process.
Is hyaluronic acid useful during microneedling?
Yes. Hyaluronic acid and sodium hyaluronate are widely used in microneedling to support skin hydration, cushion the treatment, and enhance comfort. Low-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid penetrates more deeply and helps maintain hydrated skin during recovery, while higher weights protect the surface.
Can microneedling help with acne scars and fine lines?
Yes. Microneedling improves acne scars, fine lines, and uneven skin texture by stimulating collagen production and increasing cell turnover. Combining microneedling with vitamin C, niacinamide, retinyl esters, and peptides enhances results while minimizing irritation.
How does microneedling affect sensitive or irritated skin?
When performed correctly, microneedling can actually improve sensitive skin by strengthening the skin barrier over time. However, during treatment the skin is temporarily vulnerable.
That’s why calming actives are essential:
- Panthenol
- Niacinamide
- Vitamin E
- Aloe vera extract
- Antioxidant protection ingredients
Avoid harsh chemicals, fragrances, and aggressive actives that may worsen irritation.
Does microneedling improve uneven skin tone and radiant skin?
Yes. By increasing cell turnover and improving ingredient penetration, microneedling helps reduce uneven skin tone, age spots, and dullness. Brightening vitamins such as vitamin C derivatives, vitamin K, and antioxidant properties help reveal more radiant, youthful skin over time.
What is post-treatment care after microneedling?
Post treatment care focuses on supporting the skin’s healing process:
- Keep the skin hydrated
- Use barrier-supportive skincare products
- Avoid sun exposure and harsh chemicals
- Focus on antioxidant protection and wound healing
Ingredients like vitamin E, panthenol, essential nutrients, and aloe vera help reduce irritation and speed recovery.
Can microneedling be combined with chemical peels or intense pulsed light?
Not at the same session. Combining microneedling with chemical peels or intense pulsed light too closely can overstress the skin, increase sensitivity, and slow healing. These treatments should be spaced appropriately based on skin type and recovery speed.
Is microneedling suitable for all skin types?
Microneedling can be adapted for most skin types, but depth, frequency, and active ingredients must be adjusted. Clients with active infections, damaged skin, or severe skin sensitivity require extra caution and professional evaluation.
How long does it take to see results from microneedling?
Initial improvements in skin hydration and texture may appear within days. Visible improvements in collagen production, skin firmness, and fine lines typically develop over several weeks as the body responds to the collagen induction process.
Why ingredient purity matters in microneedling skincare products
When microchannels are open, everything enters deeper layers — not just the active ingredient. That’s why active ingredients used in microneedling must be sterile, stable, and free from fragrance or unnecessary fillers to protect skin health and avoid unwanted reactions.
What makes microneedling different from a regular skincare routine?
A skincare routine works on the surface. Microneedling directly influences skin cells, cell turnover, collagen synthesis, and wound healing. Because of this, ingredient selection, pH, and formulation quality matter far more than marketing claims or ingredient trends.
Last updated on Dec 14, 2025
A new, evidence-based guide explaining how microneedling alters vitamin penetration, irritation risk, and stability—plus clear rules for safe in-treatment and post-treatment use.
Please share this post
Table of Contents
What makes a vitamin microneedling-safe🔬🧬 Vitamin A: your strongest tool — and your sharpest edge 🛡️Vitamin B: the calm, steady workhorses of microneedling✨ Vitamin C: brilliance, chemistry, and the art of choosing the right form🌿 Vitamin D: a quiet nutrient with a limited — but specific — role 🧴Vitamin E: lipid protection and calm support inside microchannels 🩸Vitamin K: vascular repair and faster recovery where it matters⚡ Vitamin-like actives: the silent performance boosters inside microchannelsMicroneedling cocktails by skin concern: your fast decision mapThe takeaway: precision winsFrequently asked questionsSalmon Sperm Facials? Inside the PDRN Trend
“Salmon sperm facial” is viral. PDRN is the science. This guide breaks down mechanisms, injectables vs topical reality, and how to turn hype into compliant, profitable protocols.
Chemistry of beauty
8 min
Vitamin C by day, vitamin A by night — the science of results
Discover why the C + A philosophy — vitamin C in the morning, vitamin A at night — creates 24-hour skin renewal. Learn how to build protocols, home care, and client plans that deliver visible firmness and lasting glow.
Chemistry of beauty
10 min
Water vs oil vs emulsion: a pro guide to vitamin delivery
Discover how water-, oil-, and emulsion-based vitamin systems change how skincare works. Learn which base fits every client, how delivery systems boost results, and how to read formulas like a chemist — for faster, safer, smarter performance.
Chemistry of beauty
11 min
Unlock FREE bonus material!
Get your hands on "Salon retail cheat sheet: scripts and psychology for pros". Subscribe to our newsletter and receive a link to download it straight to your inbox.
Oh no! We couldn’t subscribe you ☹️
Done! We've sent a link to your Email 📨
Trusted by the best in the beauty industry.
Transform your beauty business with Suplery!
Already enjoying our expert tips? Take the next step and join Suplery to revolutionize your business operations.
Huge range of professional products
One-click checkout after first order
Automated predictive orders
Seamless inventory management
From words to action
Start working with Suplery and explore all the tools and services you need to expand your business
Get started with Suplery24/7 Support
Secure payments
Designed by industry’s experts