The role of vitamins in modern cosmetics
Vitamins aren’t just about keeping the body running — they’re the hidden engine of skincare, haircare, and overall beauty maintenance. Modern cosmetology has taken vitamins beyond the dinner plate and into serums, creams, and treatments designed to enhance skin health, fight aging, and address specific concerns.
Yet, not all vitamins are created equal. Their impact depends on concentration, formulation, and stability. What makes a vitamin-infused skincare product truly effective? How do delivery mechanisms determine whether an ingredient penetrates deep into the skin or merely sits on the surface? And which vitamin combinations provide maximum benefits without irritation?
This guide unpacks the science behind vitamins in cosmetics. You'll find clear, actionable insights backed by the latest research.
The power of natural and synthetic vitamins in beauty science
Vitamins aren’t just add-ons in skincare — they’re the backbone of skin health. They regulate, repair, and protect, working at the cellular level to keep everything running smoothly.
Let’s break down what makes them so crucial and how they elevate cosmetic formulations from basic to breakthrough.
Vitamins: what they do and why they matter
Vitamins are organic compounds that fuel biochemical processes essential for maintaining healthy skin, hair, and nails. They drive cell renewal, support barrier function, and act as antioxidants.
The skin, being the body’s largest organ, responds quickly to vitamin deficiencies — dryness, flakiness, premature aging, and inflammation are common signs. The right balance of vitamins is also crucial for strong, healthy hair and nails.
Vitamin B7 (biotin) strengthens nails and hair, reducing brittleness. Vitamin C enhances collagen synthesis, helping to maintain skin firmness and elasticity.
Why are vitamins in cosmetics a game-changer?
Cosmetic chemists aren’t just adding vitamins to skincare for the sake of it — they’re harnessing their biochemical potential. Applied correctly, vitamins penetrate the skin and influence cell activity, offering anti-aging, hydrating, and protective benefits.
Vitamin A speeds up cell turnover, vitamin C shields against oxidative stress, and vitamin E locks in moisture while enhancing barrier repair.
Scientific research consistently confirms that well-formulated vitamin-based cosmetics improve skin resilience, slow aging, and fortify against environmental stressors.
How do vitamins work in skincare?
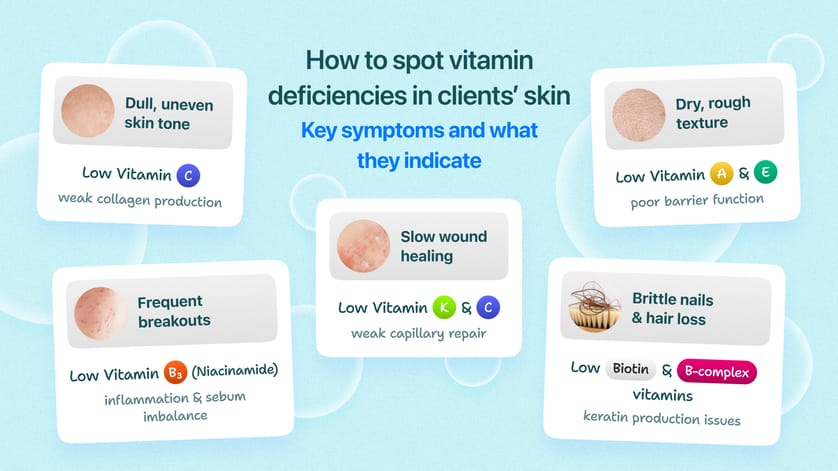
Vitamins aren’t the bricks and mortar of our cells like proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, but they run the entire construction site. They regulate growth, repair, immune response, metabolism, and aging, ensuring the body (and skin) functions as it should. When vitamins are in balance, skin stays resilient, nails grow strong, and hair thrives. When they’re missing, things start falling apart—dullness, breakouts, rough texture, and premature aging are just the beginning.
But balance is key. While vitamin deficiencies can cause dry, sluggish, and weakened skin, an overload isn’t much better. Water-soluble vitamins (like Vitamin C and B-complex) are flushed out regularly, so the body takes what it needs and discards the rest. Fat-soluble vitamins (like A, D, E, and K), however, hang around in fatty tissues and the liver, meaning too much can build up and become irritating—or even harmful.
So, what happens when the skin doesn’t get enough vitamins?
It struggles. Hydration drops, cell renewal slows, collagen production weakens, and the barrier function loses its edge. The result? Fine lines, dryness, breakouts, uneven tone, and slower healing. But give the skin what it needs, and vitamins help strengthen, hydrate, brighten, and repair, restoring balance and resilience.
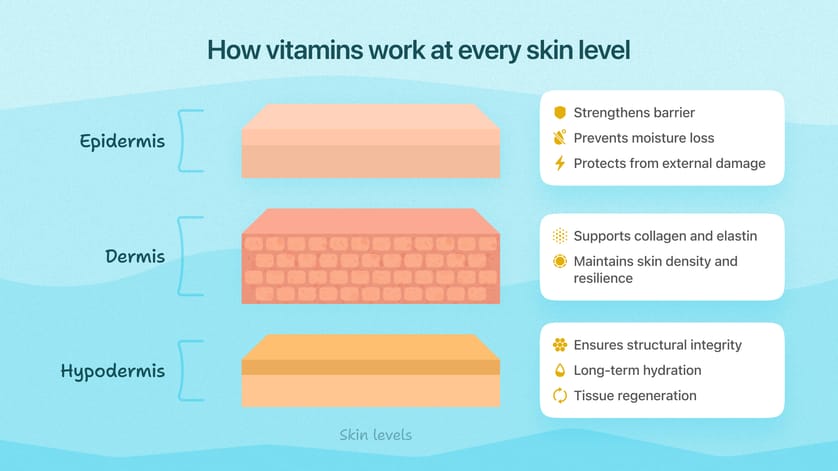
And they don’t just work on the surface. Vitamins operate at different levels of the skin, tackling issues from the outside in.
- Epidermis (surface layer): strengthens the barrier, retains moisture, and protects against environmental damage.
- Dermis (middle layer): supports collagen, elasticity, and deep hydration, keeping skin firm and plump.
- Hypodermis (deepest layer): plays a long-term role in regeneration and structure, ensuring skin stays strong over time.
Since nails and hair are extensions of the skin, they also depend on consistent nourishment. Nails form through keratinization, a process that requires steady vitamin support, while hair follicles rely on skin health to produce strong, flexible, and well-hydrated strands. Without proper vitamin supply, both nails and hair become weak, brittle, and prone to breakage.
In short? Vitamins aren’t just nice to have—they’re essential. They don’t just sit on the skin; they work throughout its layers, ensuring strength, hydration, and regeneration. The key is balance, smart formulations, and consistent supply—because when vitamins are working right, your skin, hair, and nails show it.
Vitamin C’s role in collagen production is essential for maintaining skin structure. A deficiency weakens this process, leading to sagging and fine lines.
Master your makeup game!
Ready to create stunning looks? Our ultimate makeup tool guide PDF reveals the must-have tools every pro needs for flawless results. Download now — level up your salon’s makeup services!
Oh no! We couldn’t subscribe you ☹️
Done! We've sent a link to your Email 📨
Natural vs. synthetic vitamin sources
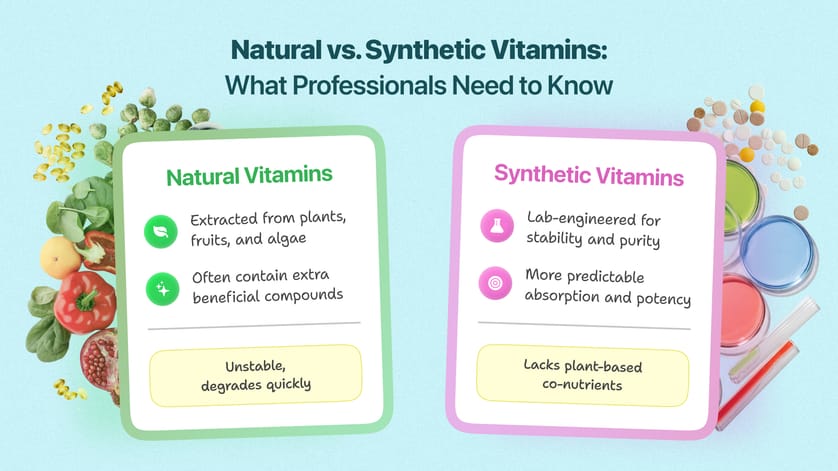
Vitamins in cosmetics can come from natural sources, extracted from plants, fruits, and algae, or they can be synthetically produced in a lab. While the word “natural” may sound appealing, the reality is that both types have their place in skincare—and sometimes, the synthetic versions are the better choice.
How are they made?
- Natural vitamins are extracted using physical or mechanical processes—think cold pressing, filtration, or distillation. These methods keep the vitamin in its natural state but often leave it unstable, sensitive to light, air, and temperature.
- Synthetic vitamins are created through a series of controlled chemical reactions, replicating the molecular structure of natural vitamins but with added stability and purity. These lab-made versions can be more efficient, bioavailable, and resistant to degradation.
Why can’t we rely only on natural vitamins?
- Stability. Many natural vitamins break down quickly when exposed to air, light, or heat, making them less effective in long-term skincare formulations. Synthetic versions can be stabilized to maintain potency from the first to the last application.
- Concentration control. Extracting vitamins from natural sources can lead to inconsistent potency—one batch might have higher concentrations than another. Synthetic vitamins ensure precise dosages, giving formulators better control over their effectiveness.
- Sustainability and availability. Some vitamins are difficult to extract in large amounts without harming the environment. For example, obtaining enough Vitamin C from fruit sources for mass production would require enormous amounts of citrus, leading to excessive waste. Synthetic Vitamin C allows for high availability without depleting resources.
- Bioavailability and absorption. Some synthetic vitamins are engineered to absorb better into the skin than their natural counterparts. For example, retinol (synthetic Vitamin A) is often more effective at stimulating collagen production than beta-carotene (its natural precursor).
So, which is better?
Neither is inherently superior—it depends on the formulation and purpose. Natural vitamins provide additional plant compounds that may offer skin benefits, while synthetic vitamins allow for greater consistency, longer shelf life, and enhanced delivery to the skin.
In the end, the best skincare formulations use both, balancing nature’s richness with science’s precision to create products that are effective, stable, and sustainable.
Lab-formulated ascorbic acid (vitamin C) is widely used in serums due to its superior stability compared to natural citrus extracts.
Professional, medical, and retail-grade cosmetics
Not all vitamin-infused skincare is created equal. The same vitamin can be a gentle daily booster or a prescription-strength treatment — it all depends on the formula and concentration. Some forms are mild enough for everyday hydration, while others are potent enough to treat acne, pigmentation, or even skin cancer. This is why skincare is divided into three categories: medical-grade, professional-grade, and retail.
- Medical-grade: these are the real deal — highly potent, clinically tested formulations used for serious skin conditions. Think prescription-strength retinoids or high-dose antioxidants. They don’t just improve skin; they reshape how it functions at a cellular level. Used wrong? Expect irritation, peeling, or worse.
- Professional-grade: stronger than your average serum but not quite prescription-level, these are the go-to for trained specialists in salons and clinics. Stripped-down vitamin C peels, potent retinol treatments, and deep-penetrating serums fall into this category. They deliver faster, more dramatic results — but only if used correctly. Overdo it, and you’ll wish you hadn’t.
- Retail: designed for daily use and broad skin tolerance, retail skincare is gentler, safer, and made for long-term maintenance. You won’t get overnight miracles, but you also won’t wake up with red, peeling skin. These products use stabilized, slow-release versions of powerhouse vitamins, keeping your routine simple and effective.
The same vitamin can be a prescription drug, an in-salon treatment, or a grocery-store face cream—it all depends on the formulation. Pick the right one, and you’ll see results. Pick the wrong one, and you’ll see your dermatologist.
Over-the-counter retinol creams typically contain 0.1% retinol, while professional formulas may reach up to 1% for deeper skin transformation.
How vitamins deliver results
Having vitamins in a product doesn’t automatically mean they’ll work. Stability, absorption, and compatibility all play a role in whether they do something or just sit there.
Now, we uncover the science behind making vitamins effective — from smart formulations to cutting-edge delivery systems.
Advanced delivery systems in vitamin-based skincare
Your skin’s first job is defense. The ultra-thin outer layer (stratum corneum) is a shield against microbes, pollutants, and unwanted compounds — but that also means many skincare ingredients struggle to get through. Vitamins, no matter how beneficial, won’t do much if they just sit on the surface. To solve this, skin chemists develop smart delivery systems that help active ingredients penetrate deeper, stay stable, and activate at the right time.
Depending on how deep the vitamin needs to go and its natural properties, formulators use different strategies.
1. Direct absorption. Some small, water-soluble vitamins can absorb directly into the skin, assuming they’re formulated correctly. However, most pure vitamin molecules are unstable or struggle to penetrate deeply, which is why more advanced systems are often needed.
2. Encapsulation and emulsions. Vitamins are often wrapped in protective carriers that shield them from degradation and help them absorb efficiently. These carriers also control the release, ensuring the active ingredient works gradually rather than all at once.
- Liposomes and nanosomes – Tiny, fat-based spheres that fuse with skin cells and enhance absorption.
- Encapsulated vitamins – These slow-release forms reduce irritation and keep unstable ingredients (like Vitamin C) from breaking down before use.
3. Prodrugs (Bioconversion systems). Some vitamins aren’t active when applied but convert into their potent form once inside the skin. This reduces irritation and ensures maximum efficacy exactly where it’s needed.
- Retinol (Vitamin A) → Retinoic Acid – Converts in the skin to trigger cell turnover and collagen production.
- Panthenol (Provitamin B5) → Pantothenic Acid – A mild, hydrating ingredient that transforms into a deeply reparative compound once absorbed.
4. Penetration enhancers. Since many vitamins struggle to penetrate the skin barrier, formulators add special compounds to push them deeper. These include:
- Fatty acids and phospholipids – help fat-soluble vitamins like A and E absorb better.
- Alcohols and glycols – temporarily loosen the skin barrier to improve penetration (though overuse can dry the skin out).
Without proper delivery, a vitamin-packed cream is just a nice-smelling moisturizer. By optimizing absorption and activation, modern formulations ensure vitamins don’t just sit on the skin—they work where they’re needed most.
Vitamin stability: what really counts
Vitamins are highly sensitive compounds that can break down when exposed to oxygen, light, heat, pH changes, or even certain ingredients. If not properly protected, they lose their potency before they even reach your skin.
To prevent this, manufacturers use different stabilization strategies depending on the vitamin’s properties:
- Encapsulation technologies – wrap vitamins in protective carriers to control release and prevent degradation.
- Bioconversion systems – use inactive precursors that transform into active forms upon application.
- Stabilizers – ingredients like ferulic acid help slow oxidation and extend vitamin activity.
- Packaging – dark glass bottles and airless pumps reduce exposure to light and air.
- Temperature control – certain formulas require cool storage to remain effective.
- Limited expiration dates – ensuring the product is used while still potent.
Even a slight change in conditions — leaving a serum open too long, exposing it to heat, or improper storage — can completely destroy its effectiveness.
Always follow storage instructions to ensure your products delivers the results it promises.
The most common vitamins and industry trends
Some vitamins have earned their place as skincare staples, while others are rising stars in beauty innovation. What’s making waves in the industry?
Let’s explore the tried-and-true essentials, the latest advancements, and how science is changing the way we use vitamins in cosmetics.
Essential vitamins in cosmetics and their functions
Each vitamin plays a specific role in maintaining healthy skin, strong nails, and resilient hair. Understanding their functions allows professionals to choose the right formulations based on individual needs.
Below is a structured breakdown of the key vitamins used in cosmetics and their benefits.
Vitamins for skin health
| Vitamin group | Key forms | Functions in skincare | Targets |
|---|---|---|---|
Vitamin A | Retinol, Retinoic Acid, Retinyl Palmitate | Accelerates cell turnover, boosts collagen, reduces pigmentation | Wrinkles, uneven texture, sun damage |
Vitamin C | Ascorbic Acid, Sodium Ascorbyl Phosphate | Powerful antioxidant, brightens, stimulates collagen | Dullness, hyperpigmentation, fine lines |
Vitamin E | Tocopherol, Tocopheryl Acetate | Shields against oxidative stress, enhances hydration | Dryness, skin barrier damage, aging |
Vitamin B3 | Niacinamide | Regulates sebum, reduces redness, strengthens skin barrier | Acne, rosacea, sensitivity |
Vitamin B5 | Panthenol | Hydrates deeply, promotes wound healing, soothes irritation | Dry, flaky, or compromised skin |
Vitamin K | Phytonadione | Strengthens capillaries, reduces redness and dark circles | Dark under-eye circles, broken capillaries |
Vitamins for nail strength and growth
| Vitamin group | Key forms | Functions | Targets |
|---|---|---|---|
Vitamin B7 | Biotin | Enhances keratin production, strengthens nails | Brittle, weak nails, peeling |
Vitamin C | Ascorbic Acid | Supports collagen synthesis for stronger nail beds | Soft, thin nails prone to breaking |
Vitamin E | Tocopherol | Moisturizes, prevents nail brittleness | Dry, peeling nails |
Vitamins for hair health
| Vitamin group | Key forms | Functions | Targets |
|---|---|---|---|
Vitamin A | Retinol, Beta-Carotene | Regulates scalp oil production, supports follicle function | Dry scalp, dandruff, weak hair |
Vitamin B Complex | Biotin (B7), Pantothenic Acid (B5), Pyridoxine (B6) | Strengthens strands, supports hair growth | Thinning, brittle hair, hair loss |
Vitamin C | Ascorbic Acid | Aids iron absorption, boosts collagen for scalp health | Weak, easily damaged hair |
Vitamin D | Cholecalciferol | Plays a role in hair follicle cycling | Hair shedding, slow regrowth |
Vitamin E | Tocopherol | Improves scalp circulation, protects against oxidative stress | Dull, fragile hair |
Safety and best practices for professional use
Vitamins may be powerful, but that doesn’t mean they’re foolproof. Use them wrong, and you risk irritation, instability, or wasted potential.
Now, we lay out the smartest ways to use vitamins effectively—ensuring both safety and results in professional skincare.
Smart vitamin combinations: what works best
Some vitamins work better when paired, while others should never be mixed. Knowing these synergies can optimize skincare routines.
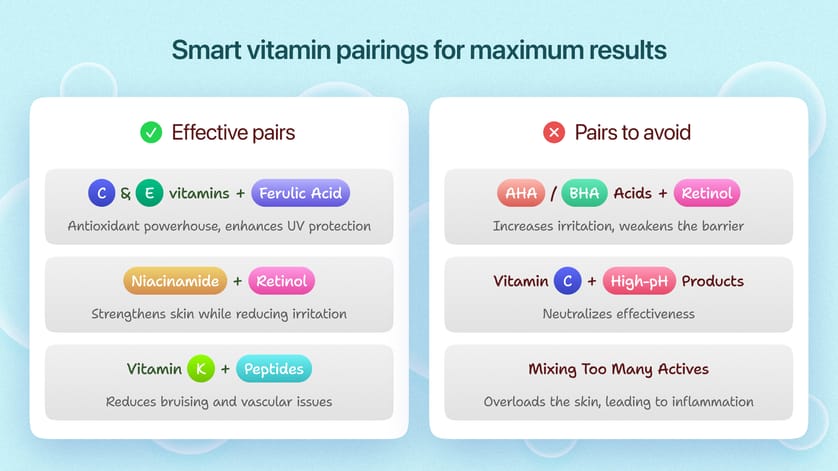
Ideal combinations:
- Vitamin C + E + Ferulic Acid: A powerhouse antioxidant blend that protects against photoaging and brightens skin.
- Niacinamide + Retinol: Reduces irritation while enhancing skin renewal and barrier function.
- Vitamin K + Peptides: Ideal for reducing bruising, swelling, and vascular concerns.
Avoid these pairings:
- Retinol + AHA/BHA Acids: Can cause excessive irritation and compromise the skin barrier.
- Vitamin C + High pH Products: Reduces vitamin C’s effectiveness, as it requires an acidic environment.
- Overloading Actives: Combining too many potent ingredients can overwhelm and stress the skin.
Managing risks: allergies and sensitivities
Certain vitamins, especially in high concentrations, can trigger adverse reactions. Best practices include:
- Conducting a patch test before full application.
- Gradually increasing the concentration of active ingredients.
- Monitoring reactions, particularly with retinoids and strong antioxidants.
- Considering skin type — sensitive skin may require lower doses of vitamin C and retinol.
Professional guidelines for vitamin-based skincare
Cosmetologists and dermatologists should follow these best practices when recommending or using vitamin-rich products:
- Assess product formulation: look beyond marketing claims and analyze the concentration and stability of vitamin components.
- Educate clients: explain how to introduce active vitamins into their routines to minimize irritation and maximize benefits.
- Seasonal considerations: retinol and high-dose vitamin C are best used in fall and winter due to increased sun sensitivity.
- Always use SPF: many vitamins, especially Vitamin A and C, make the skin more susceptible to UV damage.
- Follow scientific developments: staying informed about the latest research ensures professionals provide the best guidance and recommendations.
Suplery: the best choice for professionals
Choosing professional cosmetics isn’t just about picking a product with the right label — it’s about understanding what’s inside and how it works. That’s why Suplery provides in-depth product descriptions that break down every ingredient’s role, action, and effect.
No vague claims — just clear, factual analysis straight from the suppliers.
What you’ll find in our product cards
- Every component is explained: what it does, how it works, and how it interacts with other ingredients.
- Formulation insights: stability, absorption, and effectiveness of active ingredients like vitamins, peptides, and antioxidants.
- No marketing fluff: just the facts, so professionals can make informed decisions without exaggerated claims.
Why order through Suplery?
- Direct-from-supplier sourcing – no middlemen, ensuring up-to-date formulations and full ingredient transparency.
- Built for professionals – whether you’re a salon, clinic, or independent specialist, you get access to professional-grade products with reliable descriptions.
- Simplified ordering & inventory – easily manage orders, track stock, and reorder essentials with minimal effort.
Suplery doesn’t decide what’s best—we just make sure you have all the facts to choose confidently. Explore and compare today.
Try Suplery now
Suplery gives you clear stock visibility, instant reorder alerts, and direct access to supplier savings — so your salon stays perfectly stocked, spends less, and earns more.
Start savingWrap it up
Vitamins are indispensable in modern cosmetics, offering scientifically backed benefits that improve skin health and longevity. However, their effectiveness depends on formulation, stability, and proper use. For cosmetologists and skincare professionals, mastering the intricacies of vitamin-based skincare enables them to make informed choices, ensuring clients achieve optimal results safely and efficiently.
The future of vitamin-infused cosmetics lies in innovation — more stable formulations, smarter delivery methods, and groundbreaking combinations. By staying ahead of these advancements, professionals can leverage vitamins to their full potential, helping their clients achieve healthier, more radiant skin.
 Elevate your glow with proven beauty secrets
Elevate your glow with proven beauty secrets
Dive in now for the latest beauty hacks, expert-approved tips, and transformative routines!
Oh no! We couldn’t subscribe you ☹️
Done! You've subscribed 💛
Unsubscribe anytime. Your data is stored for business-to-business communication purposes. See our Privacy policy.
Frequently asked questions
What is the difference between natural and synthetic vitamins in skincare?
Natural vitamins in cosmetics come from natural food sources like citrus fruits, vegetable oils, and plant extracts, while synthetic vitamins are created through chemical reactions to mimic the natural ones. Both can provide essential nutrients for the skin, but natural and synthetic vitamins may differ in bioavailability, stability, and absorption.
Are synthetic vitamins as effective as natural ones in skincare?
Yes and no. Some synthetic nutrients, like ascorbic acid (Vitamin C), are chemically identical to their natural counterparts and work just as well. However, other nutrients, like natural Vitamin E (d-alpha-tocopherol), are often better absorbed by the skin compared to their synthetic counterparts (dl-alpha-tocopherol), which may have lower potency.
Why do cosmetics use synthetic vitamins instead of natural ones?
Natural vitamins can be unstable and degrade quickly when exposed to light, air, or heat. Synthetic vitamin supplements are often more stable, cost-effective, and easier to formulate in skincare products while still providing the same benefits as naturally occurring nutrients.
Is synthetic Vitamin C different from natural Vitamin C in cosmetics?
Not really. Whether it comes from citrus fruits or is lab-made, ascorbic acid has the same chemical structure. However, natural Vitamin C in cosmetics often includes additional bioflavonoids and co-factors that may enhance absorption and antioxidant activity. Some synthetic Vitamin C derivatives, like sodium ascorbyl phosphate, are designed to be more stable and better tolerated by sensitive skin.
What are the health benefits of using vitamin-infused cosmetics?
Vitamins in skincare provide essential nutrients that help with skin hydration, collagen production, antioxidant protection, and barrier repair. For example, Vitamin E protects against oxidative stress, Vitamin C boosts skin brightness and elasticity, and Vitamin D supports immune system function and helps with barrier repair.
Are natural and synthetic Vitamin E the same in skincare?
No. Natural Vitamin E (d-alpha-tocopherol) is more potent and bioavailable compared to synthetic Vitamin E (dl-alpha-tocopherol), which is a mix of different isomers with varying effectiveness. Skincare products using natural Vitamin E tend to provide better antioxidant protection and hydration.
Can synthetic vitamins in cosmetics cause skin irritation?
Some synthetic supplements, like retinyl acetate (a synthetic Vitamin A derivative), can be more irritating than their natural form. However, many synthetic ingredients in cosmetics are designed to be gentler and more stable. The key is choosing formulations that suit your skin type and sensitivity.
Do vitamin-infused cosmetics help with nutrient deficiencies?
No. While skincare with vitamins can support skin health, it cannot replace a balanced diet or fix vitamin D deficiency, folic acid deficiency, or other nutrient deficiencies. For optimal health, a nutritious diet with whole foods and dietary supplements may be necessary alongside topical skincare.
Which vitamins in cosmetics are best in their natural form?
Some fat-soluble vitamins, like Vitamin E, Vitamin D, and Vitamin A, tend to work better in their natural form because they contain other nutrients that enhance their effects. Water-soluble vitamins, like Vitamin C and B vitamins, are often just as effective in synthetic supplements as in natural sources.
Should I choose cosmetics with natural or synthetic vitamins?
Both have their pros and cons. Natural vitamins often contain additional bioactive compounds that enhance their benefits but can be less stable. Synthetic vitamins in cosmetics are often more stable, consistent, and better suited for skincare formulations. The best choice depends on skin needs, ingredient stability, and overall formulation quality.
Last updated on Mar 26, 2025
“What Changed” in this article? Everything. It's packed with the latest findings, the ripest data, and a fresh analysis you won't find anywhere else.
A subject-matter expert wrote the content, and reliable, official sources support it. Recent research has been incorporated to maintain relevancy and accuracy.
Please share this post
Table of Contents
The power of natural and synthetic vitamins in beauty scienceHow vitamins ,deliver resultsThe most common vitamins and industry trendsSafety and best practices for professional useWrap it upFrequently asked questionsSalmon Sperm Facials? Inside the PDRN Trend
“Salmon sperm facial” is viral. PDRN is the science. This guide breaks down mechanisms, injectables vs topical reality, and how to turn hype into compliant, profitable protocols.
Chemistry of beauty
8 min
Microneedling vitamins: what works, what burns, what heals
Microneedling turns vitamins into transdermal actives. Learn which vitamin forms are safe, which intensify irritation, and how pros choose formulas that heal—not complicate—treatment outcomes.
Chemistry of beauty
18 min
Vitamin C by day, vitamin A by night — the science of results
Discover why the C + A philosophy — vitamin C in the morning, vitamin A at night — creates 24-hour skin renewal. Learn how to build protocols, home care, and client plans that deliver visible firmness and lasting glow.
Chemistry of beauty
10 min
Unlock FREE bonus material!
Get your hands on "Beauty salon business plan". Subscribe to our newsletter and receive a link to download it straight to your inbox.
Oh no! We couldn’t subscribe you ☹️
Done! We've sent a link to your Email 📨
Trusted by the best in the beauty industry.
Transform your beauty business with Suplery!
Already enjoying our expert tips? Take the next step and join Suplery to revolutionize your business operations.
Huge range of professional products
One-click checkout after first order
Automated predictive orders
Seamless inventory management
From words to action
Start working with Suplery and explore all the tools and services you need to expand your business
Get started with Suplery24/7 Support
Secure payments
Designed by industry’s experts